Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout
Introduction¶
Description: This is a breakout board for Honeywell's HMC5883L, a 3-axis digital compass, provides compass heading accuracy up to 1° to 2°. Communication with the HMC5883L is simple and all done through an I2C interface. An Arduino Demo is given out to help users learn how to use this sensor.
The breakout board includes the HMC5883L sensor and all filtering capacitors as shown. This module also includes a DC regular for power supply requirement. Hence user can connect any 3.3V to 6V DC power supply.
Model: SPS05883S
Features¶
- Simple I2C interface.
- 3.3~6V supply range.
- Low current draw.
- Dimensions: 18 * 16 * 1.6mm.
Usage¶
Hardware¶
Connect this triple axis magnetometer breadkout module to your Arduino/Crowduino I2C wires(SDA:A4, D18;SCL:A5, D19)as below: 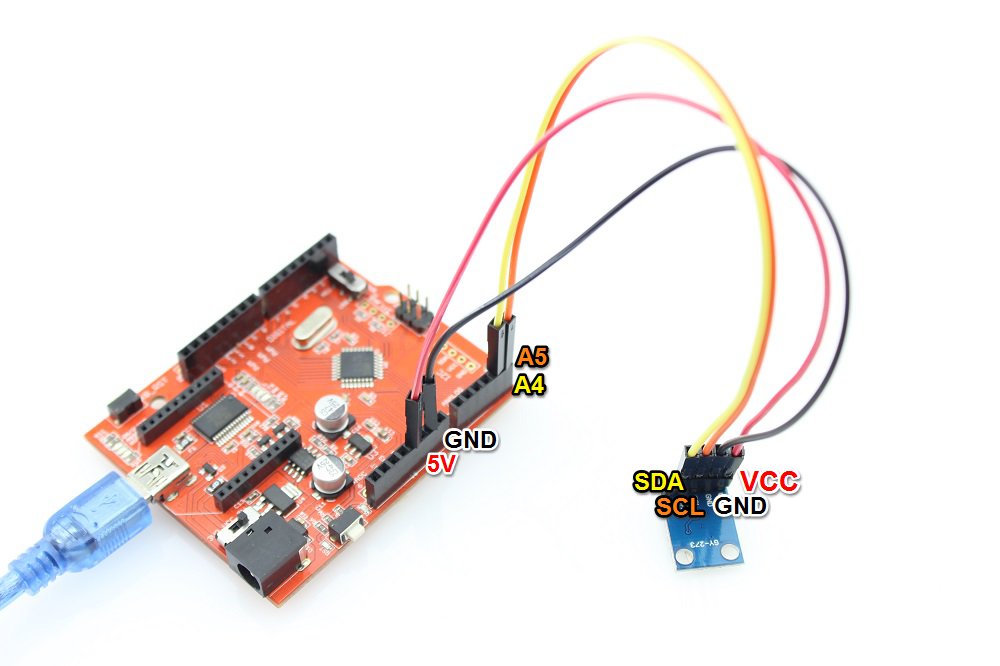
Programming¶
First download the HMC5883L library to your PC, please refer to the how to install library.
you can begin your user application program as below:
// Reference the I2C Library
#include <Wire.h>
// Reference the HMC5883L Compass Library
#include <HMC5883L.h>
// Store our compass as a variable.
HMC5883L compass;
// Record any errors that may occur in the compass.
int error = 0;
// Out setup routine, here we will configure the microcontroller and compass.
void setup()
{
// Initialize the serial port.
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Starting the I2C interface.");
Wire.begin(); // Start the I2C interface.
Serial.println("Constructing new HMC5883L");
Serial.println("Setting scale to +/- 1.3 Ga");
error = compass.setScale(1.3); // Set the scale of the compass.
if(error != 0) // If there is an error, print it out.
Serial.println(compass.getErrorText(error));
Serial.println("Setting measurement mode to continous.");
error = compass.setMeasurementMode(MEASUREMENT_CONTINUOUS); // Set the measurement mode to Continuous
if(error != 0) // If there is an error, print it out.
Serial.println(compass.getErrorText(error));
}
// Our main program loop.
void loop()
{
// Retrive the raw values from the compass (not scaled).
MagnetometerRaw raw = compass.readRawAxis();
// Retrived the scaled values from the compass (scaled to the configured scale).
MagnetometerScaled scaled = compass.readScaledAxis();
// Values are accessed like so:
int MilliGauss_OnThe_XAxis = scaled.XAxis;// (or YAxis, or ZAxis)
// Calculate heading when the magnetometer is level, then correct for signs of axis.
float heading = atan2(scaled.YAxis, scaled.XAxis);
float declinationAngle = -0.0457;
heading += declinationAngle;
// Correct for when signs are reversed.
if(heading < 0)
heading += 2*PI;
// Check for wrap due to addition of declination.
if(heading > 2*PI)
heading -= 2*PI;
// Convert radians to degrees for readability.
float headingDegrees = heading * 180/M_PI;
// Output the data via the serial port.
Output(raw, scaled, heading, headingDegrees);
// Normally we would delay the application by 66ms to allow the loop
// to run at 15Hz (default bandwidth for the HMC5883L).
// However since we have a long serial out (104ms at 9600) we will let
// it run at its natural speed.
delay(66);//of course it can be delayed longer.
}
// Output the data down the serial port.
void Output(MagnetometerRaw raw, MagnetometerScaled scaled, float heading, float headingDegrees)
{
Serial.print("Raw:\t");
Serial.print(raw.XAxis);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(raw.YAxis);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(raw.ZAxis);
Serial.print(" \tScaled:\t");
Serial.print(scaled.XAxis);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(scaled.YAxis);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(scaled.ZAxis);
Serial.print(" \tHeading:\t");
Serial.print(heading);
Serial.print(" Radians \t");
Serial.print(headingDegrees);
Serial.println(" Degrees \t");
}
Open the serial monitor, and set the baudrate to 9600, you will see the output change with the sensor orientation. 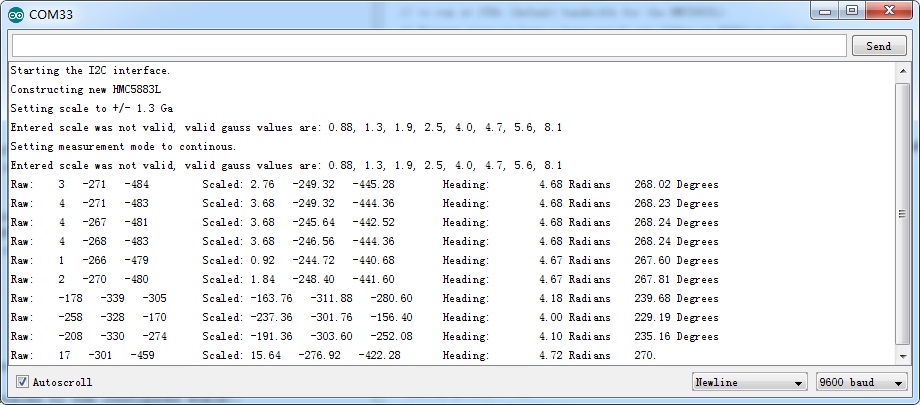
Resource¶
HMC5883L datasheet
File:Compass breakout demo code for arduino 10.zip
