Crowtail- 3-Axis Digital Gyro
Description¶
Crowtail - 3-Axis Digital Gyro module based on ITG 3200. It is the world’s first single-chip, digital-output, 3-axis MEMS motion processing gyro optimised for gaming, 3D mice, and motion-based remote control applications for Internet connected Digital TVs and Set Top Boxes. The ITG-3200 features three 16-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for digitising the gyro outputs, a user-selectable internal low-pass filter bandwidth, and a Fast-Mode I2C (400kHz) interface.
Model: CT0058ADG
Specification¶
- Supply Voltage: 3.3V, 5V
- Operation Current: 6.5mA
- Standby current: 5μA
- Sensitivity: 14 LSBs per °/sec
- Full scale range: ±2000°/sec
- Acceleration: 10,000g for 0.3ms
- On-chip temperature sensor
- Crowtail compatible interface
- Three integrated 16-bit ADCs
- ±2000°/s full scale range and 14.375 LSBs per °/s sensitivity
- Integrated amplifiers and low-pass filters
- Hermetically sealed for temp and humidity resistance
- Dimensions(mm):20.0(L)x20.0(W)x9.8(H)
Usage¶
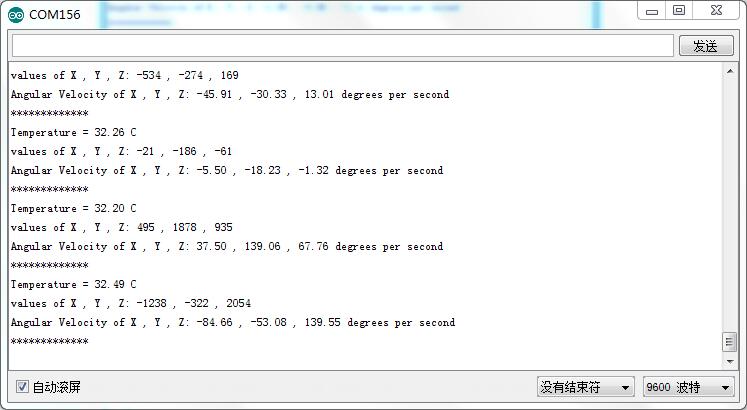
Here below we show you how to get data from this digital gyro,the data is in the unit of rad/s. 
1. Plug it onto the I2C port of your Crowtail- Base Shield.
2. Download the Crowtail- 3-Axis Digital Gyro Program and unpack it into arduino-1.0\libraries in your Arduino installation folder.
3. Open the demo code directly by the path:File -> Example -> 3-Axis_Digital_Gyro -> ITG3200_gyro.
4. Upload the code and open the serial monitor.
#include <Wire.h>
#include "ITG3200.h"
ITG3200 gyro;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
gyro.init();
gyro.zeroCalibrate(200,10);//sample 200 times to calibrate and it will take 200*10ms
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print("Temperature = ");
Serial.print(gyro.getTemperature());
Serial.println(" C");
int16_t x,y,z;
gyro.getXYZ(&x,&y,&z);
Serial.print("values of X , Y , Z: ");
Serial.print(x);
Serial.print(" , ");
Serial.print(y);
Serial.print(" , ");
Serial.println(z);
float ax,ay,az;
gyro.getAngularVelocity(&ax,&ay,&az);
Serial.print("Angular Velocity of X , Y , Z: ");
Serial.print(ax);
Serial.print(" , ");
Serial.print(ay);
Serial.print(" , ");
Serial.print(az);
Serial.println(" degrees per second");
Serial.println("*************");
delay(1000);
}
5. Open the serial monitor to check the result.