Crowtail- VL53L0X Laser Ranging Sensor
Description¶
If you want to measure something more accurate and faster. This Crowtail- VL53L0X fully meet the requirements. And the specific crowtail interface will provide convenience for us to use it with Arduino. The VL53L0X is a new generation Time-of-Flight (ToF) laser-ranging module housed in the smallest package on the market today, providing accurate distance measurement whatever the target reflectances unlike conventional technologies. It can measure absolute distances up to 2m, setting a new benchmark in ranging performance levels, opening the door to various new applications. The VL53L0X integrates a leading-edge SPAD array (Single Photon Avalanche Diodes) and embeds ST’s second generation FlightSenseTM patented technology.
The VL53L0X’s 940nm VCSEL emitter (Vertical Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser), is totally invisible to the human eye, coupled with internal physical infrared filters, it enables longer ranging distance, higher immunity to ambient light and better robustness to cover-glass optical cross-talk.
Model: CRT32115R

Features¶
- Fully integrated miniature module
- 940nm Laser VCSEL
- VCSEL driver – Ranging sensor with advanced embedded micro controller
- 4.4 x 2.4 x 1.0mm
- Fast, accurate distance ranging
- Measures absolute range up to 2m
- Reported range is independent of the target reflectance
- Operates in high infrared ambient light levels
- Advanced embedded optical cross-talk compensation to simplify cover glass selection
- Eye safe
- Class 1 laser device compliant with latest standard IEC 60825-1:2014 - 3rd edition
- Easy integration
- Single reflowable component
- No additional optics
- Single power supply
- I2C interface for device control and data transfer
- Xshutdown (Reset) and interrupt GPIO
- Programmable I2C address
Specification¶
- User detection for Personal Computers/ Laptops/Tablets and IoT (Energy saving).
- Robotics (obstacle detection).
- White goods (hand detection in automatic faucets, soap dispensers etc...)
- 1D gesture recognition.
- Laser assisted Auto-Focus. Enhances and speeds-up camera AF system performance, especially in difficult scenes (low light levels, low contrast) or fast moving video mode.
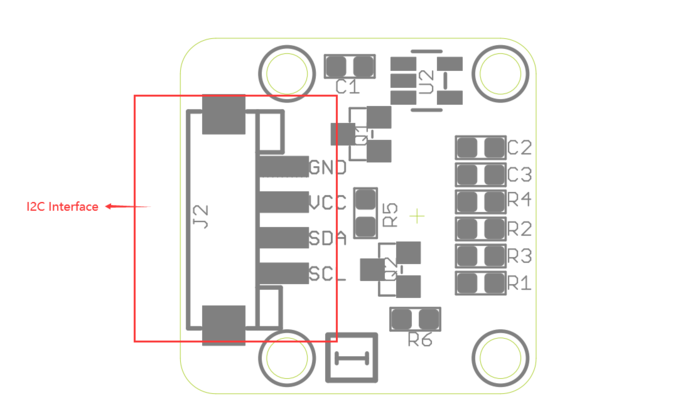
Interface¶
Platforms Supported¶
| Arduino |
|---|
 |
Usage¶
Hardware¶
STEP1 Prepare the below stuffs:
| Crowduino Uno | Base Shield | Crowtail- VL53L0X Laser Ranging Sensor |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
| Get one now | Get one now | Get one now |
STEP2 Plug Crowtail-Base Shield into Crowduino Uno;
STEP3 Connect Crowtail-VL53L0X Laser Ranging Sensor to I²C port of Crowtail-Base Shield;
STEP4 Connect Crowduino Uno to PC via a Mini USB cable.
| NOTE |
|---|
| If we don't have Crowtail Base Shield, We also can directly connect this module to Crowduino Uno as below. |
| Crowduino Uno | Crowtail- VL53L0X Laser Ranging Sensor |
|---|---|
| A4(J7) | SDA |
| A5(J7) | SCL |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
Software¶
STEP1 Download program files VL53L0X.zip
STEP2 Configure controller board&communication port
On top of the Arduino IDE, click “Tools>Board>” and select “Arduino Uno” from the available options 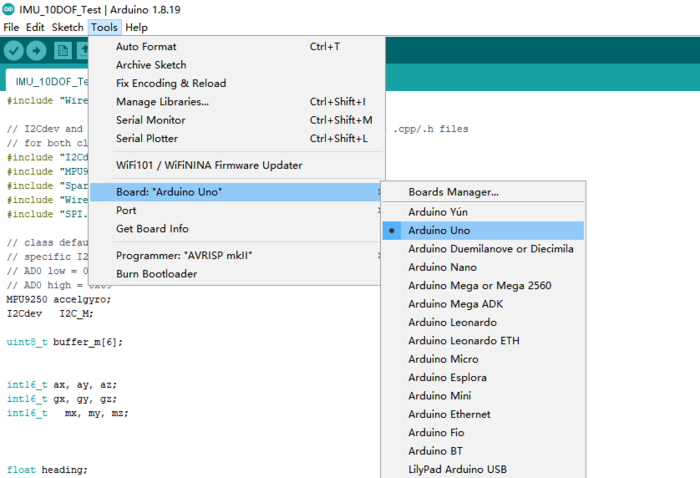
Select the COM port that indicates Arduino Uno. Please note that the actual numbers after the “COM” word will vary from computer to computer, so they could be different from the ones shown in the figure.
STEP 3 Load the program in the Arduino IDE
//the original code by Ted Meyers
//posted here: https://groups.google.com/d/msg/diyrovers/lc7NUZYuJOg/ICPrYNJGBgAJ
#include <Wire.h>
#define VL53L0X_REG_IDENTIFICATION_MODEL_ID 0xc0
#define VL53L0X_REG_IDENTIFICATION_REVISION_ID 0xc2
#define VL53L0X_REG_PRE_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD 0x50
#define VL53L0X_REG_FINAL_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD 0x70
#define VL53L0X_REG_SYSRANGE_START 0x00
#define VL53L0X_REG_RESULT_INTERRUPT_STATUS 0x13
#define VL53L0X_REG_RESULT_RANGE_STATUS 0x14
#define address 0x29
byte gbuf[16];
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
Serial.println("VLX53LOX test started.");
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("----- START TEST ----");
test();
Serial.println("----- END TEST ----");
Serial.println("");
delay(1000);
}
void test() {
byte val1 = read_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_IDENTIFICATION_REVISION_ID);
Serial.print("Revision ID: "); Serial.println(val1);
val1 = read_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_IDENTIFICATION_MODEL_ID);
Serial.print("Device ID: "); Serial.println(val1);
val1 = read_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_PRE_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD);
Serial.print("PRE_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD="); Serial.println(val1);
Serial.print(" decode: "); Serial.println(VL53L0X_decode_vcsel_period(val1));
val1 = read_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_FINAL_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD);
Serial.print("FINAL_RANGE_CONFIG_VCSEL_PERIOD="); Serial.println(val1);
Serial.print(" decode: "); Serial.println(VL53L0X_decode_vcsel_period(val1));
write_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_SYSRANGE_START, 0x01);
byte val = 0;
int cnt = 0;
while (cnt < 100) { // 1 second waiting time max
delay(10);
val = read_byte_data_at(VL53L0X_REG_RESULT_RANGE_STATUS);
if (val & 0x01) break;
cnt++;
}
if (val & 0x01) Serial.println("ready"); else Serial.println("not ready");
read_block_data_at(0x14, 12);
uint16_t acnt = makeuint16(gbuf[7], gbuf[6]);
uint16_t scnt = makeuint16(gbuf[9], gbuf[8]);
uint16_t dist = makeuint16(gbuf[11], gbuf[10]);
byte DeviceRangeStatusInternal = ((gbuf[0] & 0x78) >> 3);
Serial.print("ambient count: "); Serial.println(acnt);
Serial.print("signal count: "); Serial.println(scnt);
Serial.print("distance "); Serial.println(dist);
Serial.print("status: "); Serial.println(DeviceRangeStatusInternal);
}
uint16_t bswap(byte b[]) {
// Big Endian unsigned short to little endian unsigned short
uint16_t val = ((b[0] << 8) & b[1]);
return val;
}
uint16_t makeuint16(int lsb, int msb) {
return ((msb & 0xFF) << 8) | (lsb & 0xFF);
}
void write_byte_data(byte data) {
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.write(data);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void write_byte_data_at(byte reg, byte data) {
// write data word at address and register
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.write(data);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void write_word_data_at(byte reg, uint16_t data) {
// write data word at address and register
byte b0 = (data &0xFF);
byte b1 = ((data >> 8) && 0xFF);
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.write(reg);
Wire.write(b0);
Wire.write(b1);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
byte read_byte_data() {
Wire.requestFrom(address, 1);
while (Wire.available() < 1) delay(1);
byte b = Wire.read();
return b;
}
byte read_byte_data_at(byte reg) {
//write_byte_data((byte)0x00);
write_byte_data(reg);
Wire.requestFrom(address, 1);
while (Wire.available() < 1) delay(1);
byte b = Wire.read();
return b;
}
uint16_t read_word_data_at(byte reg) {
write_byte_data(reg);
Wire.requestFrom(address, 2);
while (Wire.available() < 2) delay(1);
gbuf[0] = Wire.read();
gbuf[1] = Wire.read();
return bswap(gbuf);
}
void read_block_data_at(byte reg, int sz) {
int i = 0;
write_byte_data(reg);
Wire.requestFrom(address, sz);
for (i=0; i<sz; i++) {
while (Wire.available() < 1) delay(1);
gbuf[i] = Wire.read();
}
}
STEP4 Click the  to upload the code to the Crowduino board
to upload the code to the Crowduino board
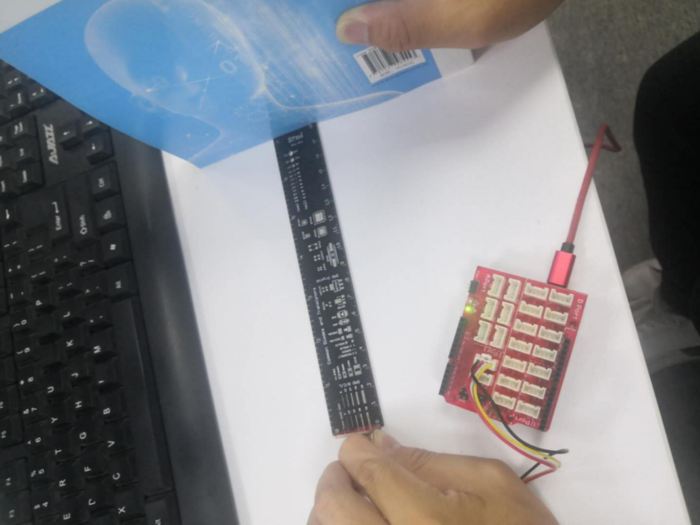
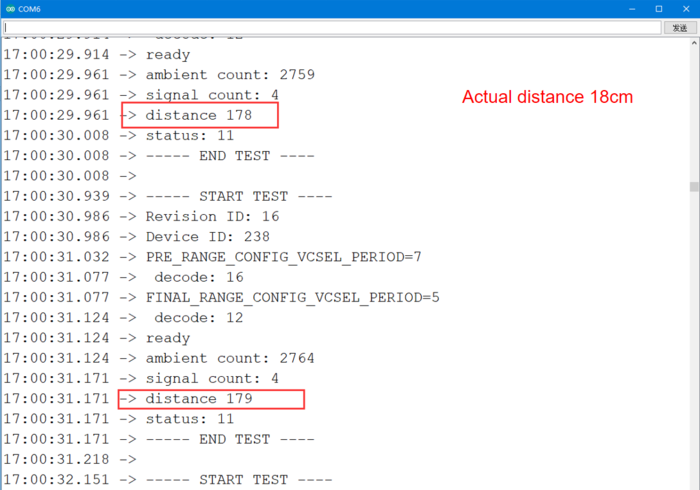
STEP5 Click the serial port monitor, set baud rate to 9600, place an object in front of the sensor, and the serial port will print out the corresponding distance, in mm. The printed distance is similar to the actual distance

FAQS¶
You can list you question here or contact with techsupport@elecrow.com for technology support.
Resources¶
Crowtail-VL53L0X_Laser_Ranging_Sensor-V2.0-Eagle.zip
VL53L0X.zip
Laser_ranging_sensor.pdf