Crowtail-GP02
Description¶
The Crowtail - GP02 module is a cost-effective and field programmable gadget. The high-performance BDS/GNSS multi-mode satellite navigation receiver SOC module, integrates RF front-end, digital baseband processor, 32-bit RISC CPU, power management and active antenna detection and protection functions. It supports a variety of satellite navigation systems, including China's Beidou satellite navigation system BDS, the United States' GPS, and Russia's GLONASS, and can realize multi system joint positioning. Model: CRT01140G

Features¶
- Field programmable
- With 32-bit RISC CPU
- Supports BDS, GPS, GLONASS
- Low power consumption
- High sensitivity and high-precision
- Can switch between GPS+BDS and GPS+GNSS modes
- Outdoor positioning
- Crowtail Indicates the compatible interface
Specification¶
- Operating voltage: DC 2.7V ~ 3.6V
- Default baud rate: 9600
- Interface type: UART
- Navigation Sensitivity: -160dbm
- Positioning accuracy: <2m(1σ)
- BDS/GPS dual mode continuous operation power consumption: 23mA
- Size(mm):40.0(L)x20.0(W)x9.7(H)
- Time to first start: Cold start: 32s ;Warm start: <1s; Hot start: <1s
Usage¶
Hardware¶
STEP1 Prepare the below stuffs:
| Crowduino Uno | Base Shield | Crowtail- GP02 |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
| Get one now | Get one now | Get one now |
STEP2 Plug Crowtail-Base Shield into Crowduino Uno;
STEP3 Plug Crowtail-GP02 to D2 D3 slot of Crowtail-Base Shield via 4 pin Crowtail Cable;
STEP4 Connect Crowduino Uno to PC via a Mini USB cable.
| NOTE |
|---|
| If we don't have Crowtail Base Shield, We also can directly connect this module to Crowduino Uno as below. |
| Crowduino Uno | Crowtail- GP02 |
|---|---|
| D2 | TX |
| D3 | RX |
| 3.3V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
Software¶
STEP1 Configure controller board&communication port
On top of the Arduino IDE, click “Tools>Board>” and select “Arduino Uno” from the available options
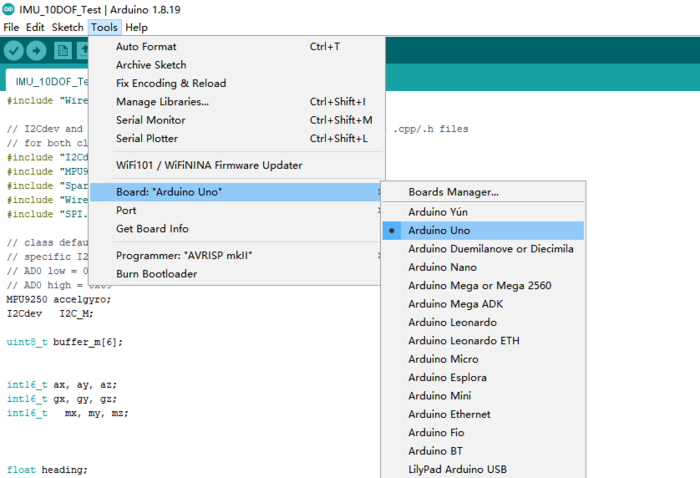
STEP2 Select the COM port that indicates Arduino Uno. Please note that the actual numbers after the “COM” word will vary from computer to computer, so they could be different from the ones shown in the figure.
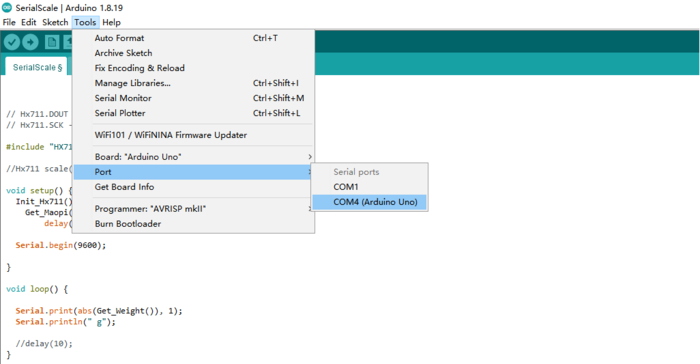
STEP3 Open the program in the Arduino IDE
//at 9600 bps 8-N-1
//Computer is connected to Arduino/Crowduino
//SoftSerial Shield is connected to the Software UART:D2&D3
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial SoftSerial(2, 3);
unsigned char buffer[256]; // buffer array for data recieve over serial port
int count = 0; // counter for buffer array
void setup()
{
SoftSerial.begin(9600); // the SoftSerial baud rate
Serial.begin(9600); // the Serial port of Arduino baud rate.
}
void loop()
{
if (SoftSerial.available()) // if date is comming from softwareserial port ==> data is comming from SoftSerial shield
{
while (SoftSerial.available()) // reading data into char array
{
buffer[count++] = SoftSerial.read(); // writing data into array
if (count == 256)break;
}
Serial.write(buffer, count); // if no data transmission ends, write buffer to hardware serial port
clearBufferArray(); // call clearBufferArray function to clear the storaged data from the array
count = 0; // set counter of while loop to zero
}
if (Serial.available()) // if data is available on hardwareserial port ==> data is comming from PC or notebook
SoftSerial.write(Serial.read()); // write it to the SoftSerial shield
}
void clearBufferArray() // function to clear buffer array
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
buffer[i] = NULL; // clear all index of array with command NULL
}
}
STEP4 Click the  to upload the code to the Crowduino board
to upload the code to the Crowduino board
STEP5 After the program is burned, open the serial monitor of Arduino IDE. Select 9600 baud rate, and the monitor will display the data returned by the GPS module. 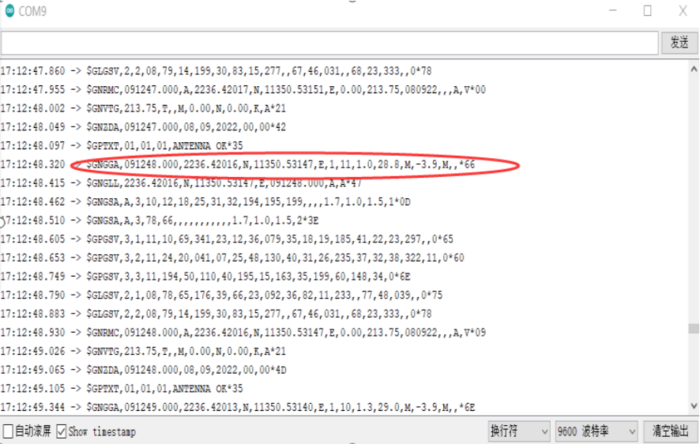
Data analysis
-
$GNGGA,(1),(2),(3),(4),(5),(6),(7),(8),(9),M,(11),(12)*HH(CR)(LF)
(1)UTC time,format: hhmmss.ss;
(2)Latitude, format: ddmm.mmmmm;
(3)Latitude hemisphere, N or S;
(4)Longitude, format: dddmm.mmmmm;
(5)Longitude hemisphere, E or W;
(6)GPS status, 0=no positioning, 1=non differential positioning, 2=differential positioning;
(7)Number of satellites in use for positioning (00~12)
(8)HDOP horizontal accuracy factor(0.5~99.9)
(9)Altitude(-9999.9~9999.9 meters)
(10)Geoid height(-9999.9~9999.9 meters)
(11)Differential time (seconds since the last time differential signal was received, non differential positioning, this item is blank)
(12) Differential reference base station label (0000 to 1023, the first 0 will also be transmitted, non differential positioning, this item is blank)
-
GPVTG ground speed information
$GPVTG,<1>,T,<2>,M,<3>,N,<4>,K,<5>*hh<1> Ground heading with due north as reference datum (000~359 degrees, the previous 0 will also be transmitted)
<2> Ground heading with magnetic north as reference (000~359 degrees, the previous 0 will also be transmitted)
<3> Ground speed (000.0-999.9 knots, the previous 0 will also be transmitted)
<4> Ground speed 0000.0 - 1851.8 km/h, the previous 0 will also be transmitted)
<5> Mode indication (only NMEA0183 version 3.00 output, A=autonomous positioning, D=differential, E=estimation, N=invalid data
-
GPGSV visual satellite status
Standard format: $GPGSV, (1), (2), (3), (4), (5), (6), (7),...) 5), (6), (7)*hh(CR)(LF)(1) Total number of GSV statement messages; 2;
(2) Current GSV full stop: 1;
(3) Total number of visible satellites: 08;
(4) PRN code (pseudorandom noise code) can also be considered as satellite number
(5) Elevation (00~90 degrees): 33 degrees;
(6) Azimuth (000~359 degrees): 240 degrees;
(7) Signal to noise ratio (00~99dB): 45dB (followed by the information of satellites 10, 16 and 17);
-
Sum check field;
hhChecksum: 78;
FAQS¶
You can post your questions on our forum or contact with techsupport@elecrow.com for technology support.
